Coronavirus and its disease state, COVID-19, seem to have taken a back seat, especially since the Russian-Ukrainian war started. That the world is weary of the pandemic is obvious given the fact that majority of countries have either relaxed or completely removed restrictions designed to curb the spread of the virus.
But, that Coronavirus has been relegated to the background does not mean that the virus has gone away. No, the virus is still very much alive and kicking. China for instance has been battling with a resurgence of the virus in Shanghai, Beijing, Hong Kong, Xi’an, Shenzhen, Dongguan, Jilin, etc. While in South Africa, two new Omicron subvariants named, BA.4 and BA.5, which are even more transmissible than the original Omicron, are causing havoc. In the USA, a third sub-variant of Omicron called BA.2.12.1 is spreading fast, especially along the East Coast.
An amino acid called L452 is part of the receptor-binding domain of the spike protein that locks onto cells, and enables the virus to gain entry into cells. All the three new Omicron variants have mutations in L452, resulting in enhanced ability to evade immune responses.
Join our WhatsApp ChannelPfizer-BioNTech and Moderna Therapeutics vaccines are regarded as gold-standards when it comes to COVID-19 vaccines, with efficacies greater than 90%. These two vaccines are based on mRNA technology, which deliver mRNA that codes for the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, to cells in the body. These cells then make copies of the spike protein, which initiate robust immune responses to clear the foreign material, SARS-CoV-2.
The key to the two mRNA vaccines is the replacement of the natural RNA building block, uridine, with a pseudouridine. Swapping the natural building block, uridine, with pseudouridine leads to higher levels of the spike protein and a lower production of the immune chemical called cytokines, known to cause side effects as in cytokine storms (a severe immune reaction often seen in autoimmune diseases, in which the body releases too many cytokines in the blood that attack the body’s own cells).
This modification stabilises the RNA, and the delivery of the N1-methyl-pseudouridine-modified mRNA encoding the SARS-COVID-19 Spike protein with a lipid nanoparticle (LNP) formulation, further solves the problem of getting mRNA into the cells. The lipid shell protects the RNA from degradation by enzymes (RNAses) or entrapment by endosomes (transporting vesicles). Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) are tiny fat bubbles used to encase messenger RNA (mRNA) that encodes a viral protein. They assist in ferrying the mRNA into cells and shield it from enzyme destruction.
READ ALSO: Death Inside Nose Masks!
But the downside of using nanoparticles to encase vaccines for delivery into the cells is that, they are a major source of unwanted side effects. When they spread through the body, they trigger headaches and inflammatory responses, which many people experience after vaccination. Not only are they the source of unwanted side effects, they are not temperature stable, and tend to fall apart at elevated temperatures, hence the Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna Therapeutics mRNA vaccines, which use LNPs to deliver mRNA into cells, have to be stored at very low temperatures, limiting their global use to only areas with facilities for low temperature storage.
Many pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies are currently experimenting with a new generation of LNPs that are more effective, have fewer side effects with increased stability, and have more precise tissue-targeting properties. It is expected that once these new generations of LNPs hit the market, most of the side effects associated with vaccination, would be eliminated.
Arcturus Therapeutics, USA, announced in late April 2022 that it had conducted a Phase 3 trial with a third mRNA-based vaccine. This vaccine is unique in that it amplifies itself! This self-amplifying ability meant that high doses of the vaccine is not required. Unlike the Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna vaccines, which use 30-microgram and 100-microgram doses, respectively, for the first two shots; only 5 micrograms of the self-amplifying mRNA is required per dose.
The vaccine trial conducted in Vietnam, showed that the new vaccine could protect against both Delta and Omicron variants. The only drawback is that the vaccine had only 55% efficacy against symptomatic COVID-19 but provided 95% efficacy against severe illness and death.
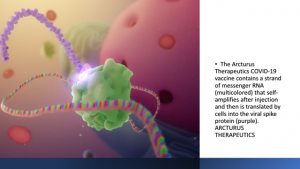
Self-amplifying vaccines use enzymes from alpha-viruses (α-viruses) to repeatedly copy the genetic strand inside a cell and the vaccines stay in the body for more than twice as long. A self-amplifying mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in theory would only require a single dose instead of multiple doses and for the fact that the vaccine is self-amplifying, it should influence more long lasting immunity than the current two mRNA vaccines. And the beauty of the new vaccine is that it can be freeze-dried for ease of transportation and storage, and only rehydrated when required.
Akash Khobragade and coworkers writing in the 2 April 2022 edition of the journal, The Lancet, reported a successful Phase 3 trial of a DNA-based vaccine called, ZyCoV-D. The vaccine is administered at a low dose of just 2 mg and contains a DNA plasmid that expresses the Wuhan Hu-1 spike antigen of SARS-CoV-2 plus an immunoglobulin (IgE) signal peptide. The vaccine, after third dose administration, showed an efficacy of 66·6% and full protection against severe illness and death. The vaccine is stable at room temperature for 2 months and has been granted Emergency Use Authorisation in India.
DNA vaccines induce adaptive immune responses, carried out by the white blood cells (lymphocytes). Such immune responses are mediated by the B cells (antibody responses) and T cells (cell-mediated responses).
However, DNA vaccines are not that popular because of challenges in delivering the vaccine into the body. Unlike mRNA vaccines that cross only the cytoplasm to reach the site where they are required, DNA vaccines need to cross the nuclear membrane and the cytoplasm. This is because the DNA needs to translocate to the nucleus for transcription (synthesis of RNA from the DNA template), followed by translation (synthesis of protein from mRNA template) in the cytoplasm. This means that the nanoparticles used in delivering mRNA vaccines do not work as well for DNA vaccines, instead the physical method of delivery is by electroporation or intradermal needle-free injection system, which is impracticable and less cost effective for large scale immunisation.
I think a little molecular biology lesson is in order here to fully explain transcription and translation terminologies above: during transcription, the genetic information contained in a strand of DNA is copied into a new molecule of messenger RNA (mRNA). The newly formed mRNA copies of the gene then serve as blueprints or templates for protein synthesis during the process of translation. In prokaryotes (represented by bacteria), transcription and translation are coupled and take place in the cytoplasm; whereas in eukaryotes (represented by humans), transcription occur in the nucleus and translation in the cytoplasm or to be precise, on the ribosome-studded endoplasmic reticulum (known as rough ER), found in the cytoplasm.
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is only found in eukaryotes, and is a sac-like structure that extends from the nuclear membrane to the cytoplasm. When complexed with ribosomes, it is called rough ER and assists in production, processing, and transport of proteins. Whereas the tubular part of the ER that lacks ribosomes, is called the smooth ER, and is involved in lipid synthesis, carbohydrate metabolism, regulation of calcium concentration, and drug detoxification.
You can now heave a sigh of relief, lesson is over. Phew!
Meanwhile last week, the World Health Organisation (WHO), released new figures showing that during the first two years of the COVID-19 pandemic (i.e. between 2020 and 2021), about 15 million people died of COVID-19. This figure is 2.7 times higher than the official reported deaths to WHO by countries. The difference between the official reported deaths and the estimated deaths, according to the journal, Nature, “is based upon estimates of excess mortality, which include deaths missed by national reporting systems”. About 84% of the estimated deaths from the virus are from southeast Asia, Europe and the Americas.
Excess mortality is obtained by statisticians and data scientists, who compare figures for the pandemic period with those of pre-pandemic years. And in countries where baseline mortality data are unavailable, global estimates of excess deaths then rely on computer models to estimate COVID-19 fatalities.
Computer modelling estimate done by The Economist magazine in London, put the figure at between 12.3 million and 21.3 million excess deaths in the period between 2020 and 2021. While the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation in Seattle, Washington, put the excess deaths for the same period at between 17.1 million and 19.6 million.
The discrepancy in the various models was due to use of different data sets and techniques. But in general, the figures of excess deaths due to the virus presented by the three bodies is staggering and sobering.
The reported figures on death from COVID-19 by WHO, also showed that India underreported deaths from COVID-19 by as much as ten times lower! Whereas India’s official reported death in the period between 2020 and 2021 was only 481,000; the new figure reported by WHO was between 3.3 million and 6.5 million! India is currently disputing this new figure.
But according to the journal, Nature, Shahid Jameel, a virologist and former chair of India’s COVID-19 genome-sequencing committee, trusts the WHO’s estimates more than the Indian government’s figures. “The ballpark [estimated] figure that India has produced so far, of about 500,000, is certainly very low. Those of us who were there and who have experienced it know that it is very low,” he says. “And now there are studies to support that.”
In other words, India is guilty of under reporting COVID-19 deaths as charged!
On Thursday 12 May 2022, the USA marked one million American deaths from COVID-19, the highest number of reported deaths in the world since the first cases of the virus were detected in January 2020. The USA with a population of 329.5 million people, has recorded more than 80 million cases of coronavirus infections, but about 220 million Americans have been fully vaccinated.
President Joe Biden called the occasion “a tragic milestone” and each death, “an irreplaceable loss”. In a televised statement, President Biden while ordering the White House flags to be lowered to half mast to mark the milestone, said, “One million COVID deaths, one million empty chairs around the family dinner table, each irreplaceable losses.”
The Peterson Centre for Healthcare and the Kaiser Family Foundation estimated that of the one million American deaths from COVID-19, about 234,000 deaths could have been prevented with vaccines.
















Follow Us